How to Stop Brute Force Attack? 10 Easy Tips to Secure Your Server

Server security is fundamental, particularly regarding sites or online organizations that depend on web-based data. Although, brute force attacks can compromise the safeguarded servers. In this guide, we will take a look at Brute Force Attack Protection.
Brute force attacks increasingly account for most cyberattacks worldwide as remote work becomes more prevalent. These are the attacks where cybercriminals target authentication mechanisms to uncover hidden or protected content in a web application or mobile app.
KemuHost’s Dedicated Servers are fully protected against such attacks with a pre-configured protection system. Additionally, we install an anti-virus application on demand without any additional cost to the customers.
What is a Brute Force Attack?
Brute Force is a sort of attack where a hacker attempts to access confidential web application data and accounts through mechanized server requests that count a list of possible solutions to a problem statement. It utilizes trial-and-error to guess login information, encryption keys, or find hidden web pages. The hackers work through all possible arrangements hoping to guess correctly. Brute Force makes these assaults, i.e., they use excessive attempts to force their way into your private account.
The ordinary brute force example is password-guessing attacks, where hackers try to discover a password by going through mixes of letters, numbers, and symbols until they find the correct pattern. They automate the process with bots, which can try different combinations much faster than humans ever could.
Approximately 81% of confirmed data breaches are due to weak or stolen passwords. So, always use a strong password with a combination of upper-lower alphabets, numbers, and special symbols.
What is a Server Brute Force Attack?
Server brute force attack is a form of hacking in which hackers try to access the entire system by trying various passwords and login combinations.
Server brute force attacks can likewise happen when an attacker attempts to figure out the login credentials for the common accounts such as administrator, admin, root, etc. The password guessing techniques used in server brute force attacks include dictionary attacks and username enumeration.
How to Determine Brute Force Attacks?
You might be right if you think somebody is attempting to break into your server or steal your information. But, there is most likely a lot more straightforward clarification. Several most common attacks are brute force attacks.
A brute force attack is easy to recognize and examine; for Linux servers, you can detect them using Apache access logs or Linux log files. For Windows Server, you can detect such attacks from Event Viewer ⇒ Security logs. The attacks will leave a series of unsuccessful login attempts. The log entries look like:
Aug 10 10:10:10 host pureftpd[89755]: yourserver (usersip[usersip]) – USER theusername (Login failed): Incorrect password.
How to Prevent Brute Force Attacks?
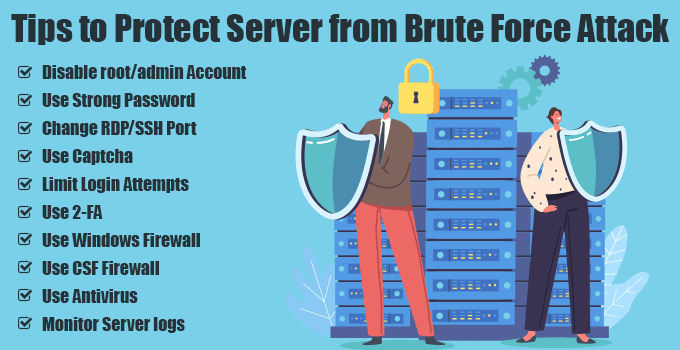
Prevention is better than cure. There are undoubtedly many ways to prevent brute force attacks. When investing more in a dedicated server, you should apply quick tips to prevent possible brute-force attacks. Let’s explore.
1) Disable root/admin Account

Mostly such attacks are made on the server with the default user accounts, i.e., admin, administrator, root. Therefore, you should keep these accounts disabled by default to reduce the attacks.
When the hacker runs the script to hack such an account, it will not find any such user active in your system. It will make your server safe and reduce the burden of overloading the system due to such extensive login attempts.
You can disable admin users from the user management option in the Windows system. In addition, you can disable Root Login from the SSH configuration file in the Linux system. Then create another user with the required privileges and use it for your routine server access.
2) Use Strong Password

Many people have cultivated a habit of setting up an easy and same password for all login accesses. But, such an easy password can be easily compromised.
Setting a solid password for all accounts is essential for Brute Force Attack Protection. One should set the password with a minimum of 8 characters with the combination of upper-lower alphabets, numbers, and special symbols.
As a server admin, you should set a complex password policy for the server that does not allow your server users to set a weak password.
3) Change RDP/SSH Port
Most automated RDP or SSH attacks are made on the default port. For example, the default RDP port of the windows system is 3389, and the default SSH port of the Linux system is 22.
The brute force attacks are generally made on these default ports to gain system access. Therefore, changing the default RDP/SSH port will undoubtedly secure your system against brute force attacks on the default ports.
In the Windows system, you can change the default RDP port from ⇒ Registry Editor ⇒ HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE ⇒ SYSTEM ⇒ CurrentControlSet ⇒ Control ⇒ Terminal Server ⇒ WinStations ⇒ RDP-Tcp ⇒ PortNumber. Set it to the random one and restart the server once.
In the Linux system, you can change the default SSH port from ⇒ /etc/ssh/sshd_config file. Set it to the random one and restart the SSH service.
Important: If you are using your server remotely, do not forget to allow that new port in the firewall before updating the configuration, or you will lose the server connection.
4) Use Captcha
You might think about how a captcha can prevent brute force attacks on the server. For example, if you have hosted a website on your server, you should use a captcha on the login, registration, and other forms.
Captcha is a security question used to verify the request from a genuine user and not the automated bots. It is generally a series of pictures or letters a user must answer to submit the form.
The captcha will prevent all bot traffic on your site and your server from being the target of brute force attacks.
5) Limit Login Attempts

By default, most websites, especially if they run on any CMS like WordPress, allow unlimited login attempts. But unfortunately, it can cause the server to be a victim of brute force attacks.
As a website administrator/developer, you should restrict login attempts. For example, you can set the fail login attempt limits to 5. Any user making more than 5 failed login attempts will be automatically blocked from making the new attempt.
For CMS like WordPress, you can find the plugin that will make this job easy.
6) Use 2-FA
Two-factor or multi-factor authentication adds an extra security layer to your accounts. It is a security feature that uses two pieces of information to unlock a user’s account.
When 2FA is enabled in your account and you try to log in to your account, apart from the username and password, the system will send a unique one-time password to your mobile or email address to confirm login access. Once you supply the correct code, you can only gain system access.
7) Use Windows Firewall

The Windows server comes with a built-in Windows Firewall with great security features. At KemuHost, we do provide Windows Dedicated Server with a fully-configured firewall.
Using Windows Firewall, you can harden the security with significantly fewer efforts. It is a powerful security tool that can help protect your server from malware and other online threats. You can restrict IP addresses and ports for both incoming and outgoing traffic. It prevents unauthorized access to your server, protects the data from being stolen, and keeps spyware and other malicious software installed on your computer.
8) Use CSF Firewall

You can install CSF – Config Server Firewall with a Linux server. It is an open-source firewall, meaning you do not need to pay for it.
CSF offers a wide range of security options such as Port Blocking, IP Blocking, Dynamic Host Blocking, Excessive Connection Blocking, Intrusion Detection System, SYN Flood Protection, Port Scan Tracking and Blocking, Exploit Checks, and many more.
If you purchase a Linux Dedicated Server from KemuHost, we will install and set up the firewall for you without additional cost.
9) Use Antivirus
Most Antivirus applications protect against most server attacks, including Brute Force attacks.
Each antivirus application has its sophisticated algorithm to block attacks before they even happen. It keeps your server safe from unauthorized access and protects your data.
At KemuHost, we install and set up the antivirus application in both Linux and Windows systems per the client’s requirement.
10) Monitor Server logs

You should analyze your log files diligently. Keep an eye on the server log files to identify suspicious behavior. For example, if you notice an increased number of logins or attempted logins from unknown users, take action to protect your system.
Log files will tell you everything. Therefore, you should regularly read the log files to track any suspicious activity and take action to prevent them.
Brute Force Attack Prevention – The Conclusion
Talented and tireless attackers will constantly try to find a way to break in. In any case, executing a combination of the above methods minimizes the possibility of you becoming a victim of brute force attacks.
KemuHost’s Dedicated Servers provide all required tools for Brute Force Attack Protection. So what are you waiting for? Get your secure server today.


